Service Workflow
The following figure describes the high-level Service workflow in the OOTB system.
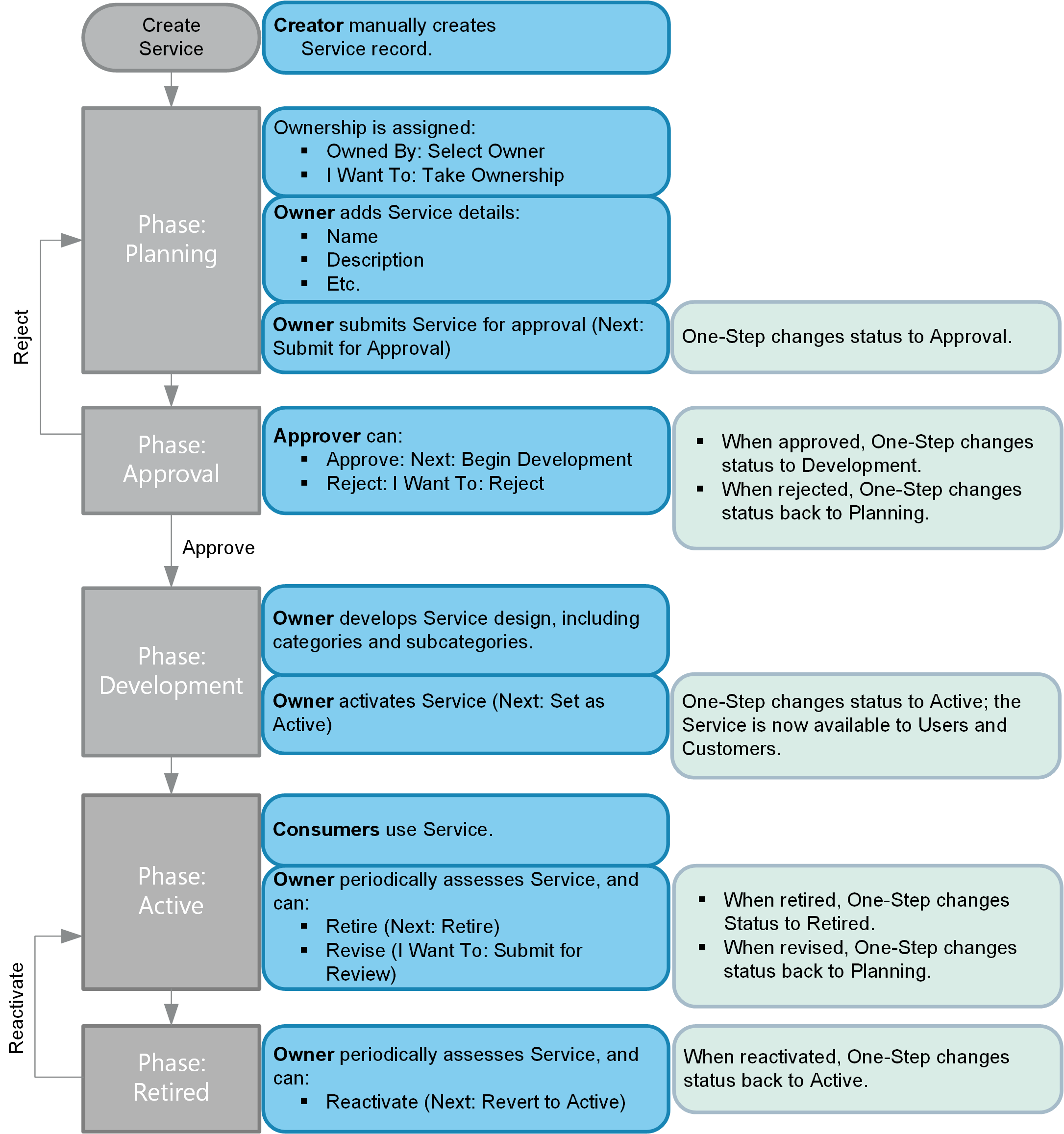
Note: CSM uses several features to enhance the Service workflow (ex: The
Service Form helps create and manage Services,
One-Step Actions help move a Service through its workflow, etc.).
Contributors
A Service typically involves the following contributors. Depending on your workflow and the size of your company, many of these contributors might be combined into one person (ex: Creator and owner might be the same person):
- Creator: User who creates the Service. This is typically a member of the Services Team.
- Owner: User who manages the Service. This is typically a member of the Services Team.
- Approver: User who ensures that the Service is ready to be released and made operational in a live environment. This is typically the Service/IT Manager.
- Consumer: Person who uses the Service. This is typically a Customer or User (technician) logging a record.
Phases
The Service workflow is broken down into the following phases:
- Planning: Creator creates a new Service. Ownership is assigned. Then, the owner designs the Service and submits it to an approver for approval to develop.
- Approval: Approver approves the Service for development. The approver can also reject the Service and send it back for rework.
- Development: Owner defines categories and subcategories for the Service. When ready, the owner releases/activates the Service.
- Active: Service is operational in a live environment. Service is periodically assessed by the owner. Service can be sent back for review/rework or be retired if necessary.
- Retired: Expired/out-of-date Service is retired. Service can be reactivated, if necessary.
Statuses
A Service progressing through the workflow encounters the following statuses:
- Planning: Service is being created, assigned an owner, designed, and submitted for Approval.
- Approval: Service is being approved by the approver.
- Development: Service is being developed (refined).
- Active: Service is operational in a live environment.
- Retired: Service is retired from use.
Note: Service phases align with Service statuses, but this is not the case in every process (ex: Incident phases are different than Incident statuses).
