Knowledge Article Workflow
The following figure shows the high-level KA process workflow in the OOTB system.
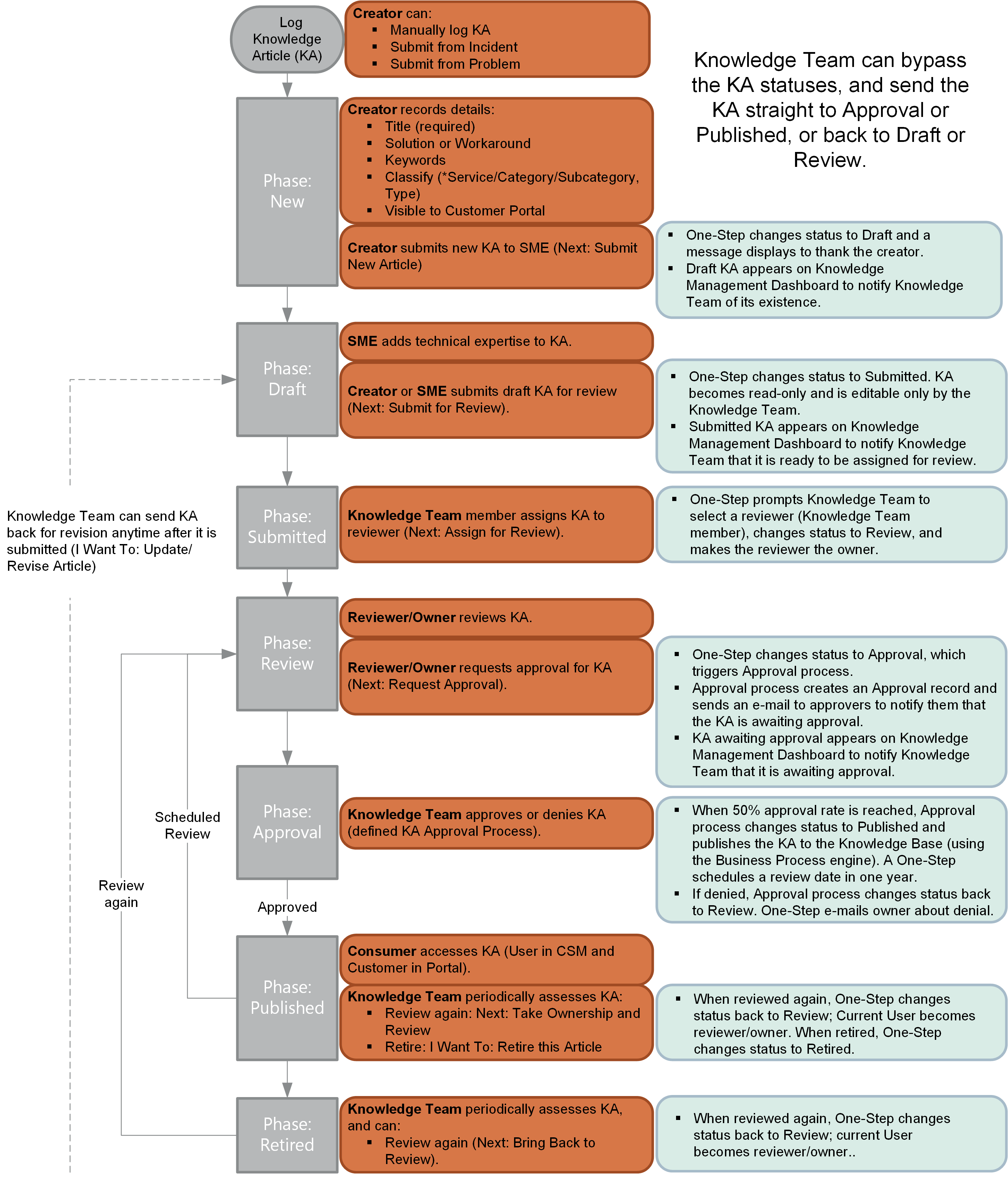
Note: CSM uses several features to manage the KA workflow (ex: The
Knowledge Article
Form helps create, manage, track, and use KAs,
One-Step Actions help move the KA through its workflow, Automation Processes
notify stakeholders via e-mails, an
Approval
Process enforces Approvals, a
Knowledge
Management Dashboard notifies stakeholders and tracks analytics, etc.).
Contributors
A KA typically involves the following contributors. Depending on your workflow and the size of your organization, many of these contributors might be combined into one person:
- Creator: User who first logs the KA.
- Subject Matter Expert (SME): User who adds technical expertise to the KA.
- Owner: User who manages the KA. This is typically a member of the Knowledge Team. By default, the Reviewer is the owner (see Reviewer).
- Reviewer: User who ensures that the KA follows company protocol. This is typically a member of the Knowledge Team.
- Approver: User who ensures that the KA is ready for publication/distribution. This is typically one or more members of the Knowledge Team.
- Publisher: User who publishes the KA so that it is available to Users and Customers. This is typically a member of the Knowledge Team.
- Consumer: User or Customer who searches for and uses the KA.
Phases
The KA workflow is broken down into the following phases:
- New: Creator logs a new KA, adding as much information as possible. Creator assigns ownership to himself or another User/Team if necessary. Then, creator submits the KA to a SME to add technical expertise.
- Draft: SME adds technical expertise to the KA. Then, SME submits the KA to the Knowledge Team for assessment/review.
- Submitted: Knowledge Team assigns a reviewer from the Knowledge Team (Reviewer becomes owner).
- Review: Knowledge Team reviewer reviews the KA to ensure that the KA follows company protocol. Then, reviewer submits the KA to the Knowledge Team for approval.
- Approval: Knowledge Team approves the KA (KA is automatically published as a result of a defined Approval Process (50% or more approve)). The Knowledge Team can also deny or abstain from approval. If denied, the KA status changes back to Review and the owner is sent an e-mail, notifying her of the denial. If abstained, the KA remains inactive until published or denied. A Knowledge Team member can manually publish the KA, if needed.
- Published: KA is operational in a live environment and available to consumers. KA is periodically assessed by the Knowledge Team (KA can be sent back for review/rework or retired, if necessary).
- Retired: Expired/out-of-date KA is retired (this status appears only after a KA is retired). KA can be un-retired (sent back for review/rework), if necessary.
Statuses
A KA progressing through the workflow encounters the following statuses:
Note: KA phases align with KA statuses but this is not the
case in every process (ex: Incident phases are different than Incident
statuses).
- New: KA is being created and submitted to a SME.
- Draft: KA is being enhanced by a SME and submitted for assessment/review.
- Submitted: KA is being assessed by the Knowledge Team and assigned to a reviewer (reviewer becomes owner).
- Review: KA is being reviewed by a member of the Knowledge Team.
- Approval: KA is being approved by the Knowledge Team, and then published.
- Published: KA is operational in a live environment.
- Retired: KA is retired from use.
